- ISRO successfully launched the second-generation navigation satellite series from the second launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre.
- NavIC is an Indian regional satellite navigation system similar to GPS that provides accurate and real-time navigation in India.
- It offers navigational services for both general and strategic users, including the armed forces. The system was developed to meet the growing needs of the Civil Aviation sector.
- NavIC is utilized in various domains such as terrestrial, aerial, and marine transportation, location-based services, personal mobility, resource monitoring, surveying and geodesy, and scientific research.
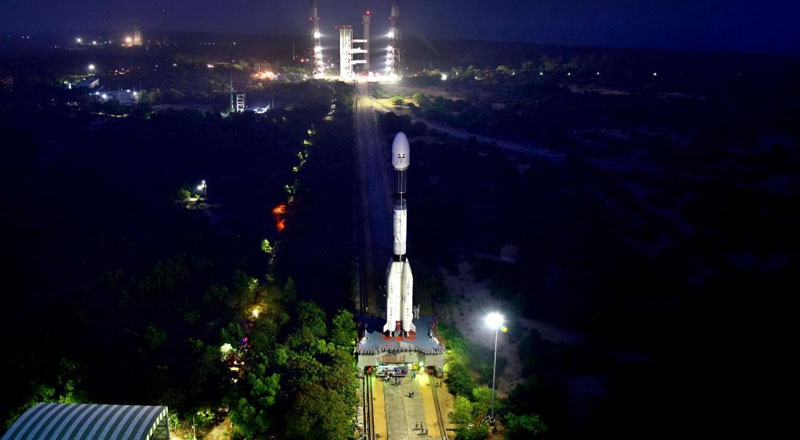
The Indian Space Research Organization (ISRO) successfully launched the second-generation navigation satellite series from the second launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre (SHAR), about 130 km from Chennai. This significant launch would guarantee that NavIC (Navigation with Indian Constellation) services will continue to operate.
NavIC is an Indian regional satellite navigation system similar to GPS that provides accurate and real-time navigation in India and a region that extends 1,500 kilometers around the Indian mainland.
The positioning and timing accuracy of NavIC signals are intended to be better than 20 meters and 50 nanoseconds, respectively. The 51.7 -meter-tall Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle, which was on its 15th flight, carried the navigation satellite NVS-01 weighing 2,232 kg.
According to ISRO, the rocket is scheduled to deploy the satellite in a geosynchronous transfer orbit (GTO) at an altitude of approximately 251 kilometers nearly 20 minutes after the flight.
What is NavIC?
NavIC, developed by Isro, is a regional navigation satellite system consisting of seven satellites in orbit, working in conjunction with ground stations. It offers navigational services for both general and strategic users, including the armed forces. The system was developed to meet the growing needs of the Civil Aviation sector in India, specifically for improved positioning, navigation, and timing. The coverage area extends beyond India’s borders, reaching up to 1500 km.
NavIC is utilized in various domains such as terrestrial, aerial, and marine transportation, location-based services, personal mobility, resource monitoring, surveying and geodesy, scientific research, time dissemination and synchronization, as well as safety-of-life alert distribution.
Weighing 2,232 kilograms, NVS-1 launched aboard the Geosynchronous Satellite Launch Vehicle (GSLV) from the second launch pad at the Satish Dhawan Space Centre in Srihari Kota. Once deployed in the Geosynchronous Transfer Orbit, the spacecraft will undergo several orbit-raising manoeuvres to position itself in the desired orbit around the Earth.
This launch marks the ninth mission for GSLV with the indigenous cryogenic stage. The rocket stands 51.7 meters tall and has a lift-off mass of 420 tonnes. It is expected to reach an apogee of 36,568 kilometers, with the payload separating approximately 18 minutes after lift-off.
(With inputs from agencies)